
CNC MILLING
Milling itself is a machining process similar to both drilling and cutting, and able to achieve many of the operations performed by cutting and drilling machines.

CNC TURNING
CNC Turning is a manufacturing process in which bars of material are held in a chuck and rotated while a tool is fed to the piece to remove material to create the desired shape.

LASER ENGRAVING
Laser engraving, which is a subset of laser marking, is the practice of using lasers to engrave an object. Laser marking, on the other hand, is a broader category of methods to leave marks on an object, which also includes color change due to chemical/molecular alteration, charring, foaming, melting, ablation, and more.

PRESS BRAKE BENDING
A press brake is a machine tool for bending sheet and plate material, most commonly sheet metal. It forms predetermined bends by clamping the workpiece between a matching punch and die. Bending process.

METAL CASTING
Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify. The solidified part is also known as a casting, which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process.

PLASTIC INJECTION
process for producing parts by injecting material into a mould. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals, (for which the process is called die-casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers.
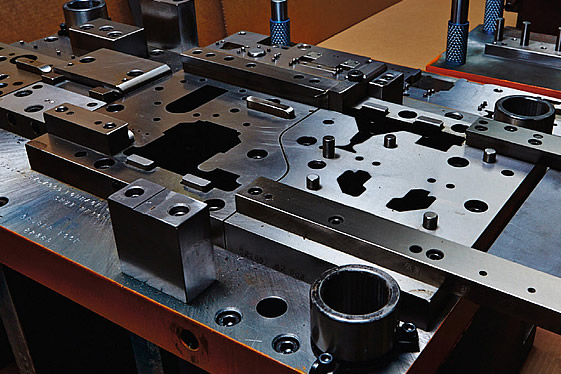
TOOL AND DIE
Tool and die makers are a class of machinists in the manufacturing industries who make jigs, fixtures, dies, molds, machine tools, cutting tools, gauges, and other tools used in manufacturing processes.

STAMPING
Stamping (also known as pressing) is the process of placing flat sheet metal in either blank or coil form into a stamping press where a tool and die surface forms the metal into a net shape. Stamping includes a variety of sheet-metal forming such as punching, blanking, embossing, bending, flanging, and coining.

RIVETING
Orbital forming machines offer the user more control over the riveting cycle but the trade off is in cycle time which can be 2 or 3 seconds. 3 different types of machine has unique features and benefits. The orbital riveting process is different from impact riveting and spiralform riveting.

SURFACE GRINDING
Surface grinding is used to produce a smooth finish on flat surfaces. It is a widely used abrasive machining process in which a spinning wheel covered in rough particles (grinding wheel) cuts chips of metallic or nonmetallic substance from a workpiece, making a face of it flat or smooth.

CYLINDRICAL GRINDING
The cylindrical grinder is a type of grinding machine used to shape the outside of an object. The cylindrical grinder can work on a variety of shapes, however the object must have a central axis of rotation. This includes but is not limited to such shapes as a cylinder, an ellipse, a cam, or a crankshaft.

THREAD ROLLING
Thread rolling is the preferred method for producing strong, smooth, precise, and uniform external thread forms. Thread rolling is different from other types of threading processes like cutting, grinding, and chasing. Thread rolling is a cold forging process that can be performed on any ductile metal.

SPOT WELDING
Spot welding is the most economical way to join two pieces of sheet metal. While joining sheet metal is the most common use for the process, resistance welding (RW) equipment actually can be used for a large variety of joining and heat-treating projects, some of which are not so well-known.

MIG WELDING
Gas metal arc welding (GMAW), sometimes referred to by its subtypes metal inert gas (MIG) welding or metal active gas (MAG) welding, is a welding process in which an electric arc forms between a consumable wire electrode and the workpiece metal(s), which heats the workpiece metal(s), causing them to melt and join.

TIG WELDING
Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), also known as tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding, is an arc welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld.

DRILL AND TAPPING
Drilling and tapping are two distinct actions. Drilling refers to creating a smooth hole in a material with a drill and motor. Tapping is the action that creates a thread into the side of the hole.

